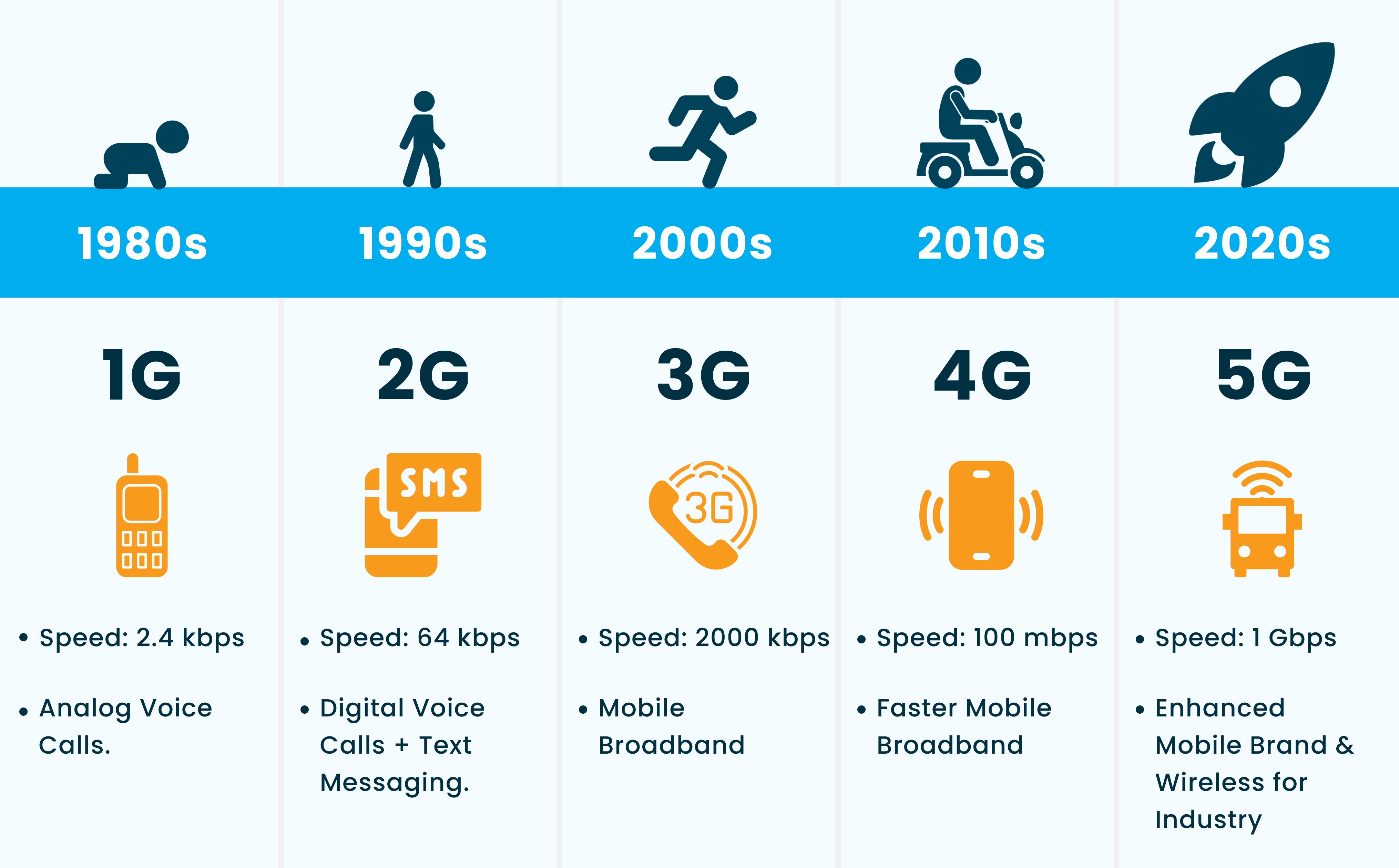
The evolution of wireless technology from 1G to the upcoming 6G. Each generation, from 1G to 5G, has brought advancements in data speeds and capabilities, expanding the possibilities of wireless communication. The shift from fixed landlines to mobile communication has enabled instant connectivity and mobility. With each generation, we have seen progress in terms of data services and internet access.
The upcoming 6G technology is expected to revolutionize the way we connect and interact with the world. It promises lightning-fast data transmission and introduces innovative applications like human digital twins, holographic communication, and extended reality experiences. 6G is envisioned as a technological frontier where artificial intelligence, millimeter-wave channels, and visible light communication converge to redefine how we communicate, connect, and perceive our surroundings.
1G: The Pioneering Era (1979-1990s)
The story begins with 1G, the first commercially launched cellular network technology in the late 1970s. Developed in Japan and later adopted in the US, 1G was a significant leap forward, enabling mobile voice communication for the first time. However, compared to today’s standards, its limitations were numerous.
- Analog Technology: 1G relied on analog signals for transmission, susceptible to interference and offering poor voice quality. Imagine crackling phone calls and dropped connections – a far cry from the crystal-clear audio we experience today.
- Limited Speeds: Data transfer rates were abysmally slow, hovering around 2.4 kilobits per second (kbps). This meant tasks like sending a text message, a basic function on any modern phone, would have been an excruciatingly slow process.
- Network Capacity: The capacity of 1G networks was extremely limited, meaning only a small number of users could be connected simultaneously in a given area. This often resulted in congested networks and dropped calls, especially in populated areas.
- Limited Functionality: 1G was purely designed for voice calls. There was no concept of data services like internet access or mobile apps, functionalities that define today’s mobile experience.
2G and 3G: Stepping Stones to the Information Age (1990s-2000s)
The limitations of 1G paved the way for the development of 2G and 3G networks. These advancements introduced digital signals, significantly improving voice quality and paving the way for basic data services like SMS (text messaging) and rudimentary internet access.
- Digital Signals: The shift to digital technology in 2G networks improved call clarity and reduced interference. Additionally, it enabled features like caller ID and voicemail, functionalities that seem commonplace today but were revolutionary back then.
- Birth of Data Services: 2G introduced functionalities like SMS and low-speed internet access, allowing for basic data transmission. While speeds were still slow (around 50-100 kbps), it marked the beginning of mobile data usage.
- The Rise of 3G: 3G networks further improved data transfer rates, reaching speeds of up to 2 Mbps. This enabled functionalities like basic web browsing, email access, and the downloading of small multimedia files. However, these tasks were still relatively slow and cumbersome compared to today’s standards.
The 4G Revolution: Ushering in the Mobile Broadband Era (2000s-2010s)
The arrival of 4G networks in the late 2000s marked a significant leap forward in mobile technology. 4G introduced advancements that fundamentally changed how we use our mobile devices:
- High-Speed Broadband: 4G offered significantly faster data speeds, reaching up to 100 Mbps and beyond. This enabled activities like streaming music and video, video conferencing, and real-time online gaming – experiences unimaginable by previous generations.
- Mobile App Explosion: The high bandwidth of 4G networks fueled the explosion of mobile apps. Users could now download and use a vast array of applications, transforming mobile devices into powerful tools for communication, entertainment, and productivity.
- The Rise of Social Media: 4G’s capabilities fueled the rise of social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. These applications, requiring constant data connection and file sharing, wouldn’t have been possible with the limitations of earlier technologies.
The Arrival of 5G: A New Era of Connectivity (2010s-Present)
5G, the latest iteration of wireless technology, represents a quantum leap forward in mobile communication. It builds upon the foundation laid by its predecessors, offering unprecedented speed, capacity, and responsiveness:
- Ultra-Fast Speeds: 5G boasts theoretical speeds exceeding 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps), making it hundreds of times faster than 4G. This allows for near-instantaneous downloads, uploads, and streaming of high-definition content.
- Ultra-Low Latency: Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel between devices. 5G offers significantly lower latency compared to previous generations, enabling real-time applications like remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and advanced virtual reality experiences.
- Massive Network Capacity: 5G networks can accommodate a significantly higher number of connected devices compared to 4G. This is critical for the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), where billions of devices will be interconnected and generating data.
Beyond Speed: The Impact of 5G on Different Sectors
The transformative potential of 5G extends far beyond enabling faster downloads and uploads. It has the potential to revolutionize various sectors of the economy and society:
- Smart Cities: 5G can facilitate the development of smart cities, where infrastructure and services are interconnected and optimized. This can include intelligent traffic management systems, real-time environmental monitoring, and connected utilities.
- Industrial Automation: 5G’s low latency and high bandwidth enable remote monitoring and control of industrial processes in real time. This can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize production in factories and manufacturing plants.
- Healthcare: 5G has the potential to transform healthcare delivery. Remote surgeries, real-time patient monitoring, and connected medical devices are just a few examples of how 5G can improve medical care and save lives.
- Agriculture: 5G can empower precision agriculture by enabling real-time monitoring of soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. This allows farmers to optimize resource usage and improve yields.
Also Read: How Does 5G Technology Enhance The Internet Of Things (IoT)?
Challenges and Considerations for 5G Deployment
While 5G offers immense potential, there are challenges associated with its widespread deployment:
- Infrastructure Development: Building and maintaining a robust 5G network infrastructure requires significant investment. This includes the installation of new cell towers, fiber optic cables, and specialized equipment.
- Device Compatibility: Not all current mobile devices are compatible with 5G networks. Users will need to upgrade their devices to fully leverage the benefits of 5G.
- Security Concerns: The increased complexity of 5G networks introduces new security vulnerabilities. Robust cybersecurity measures are necessary to protect user data and critical infrastructure.
Application of 5G Technology
IoT
5G technology allows Internet of Things (IoT) devices to quickly send large amounts of data, which enables real-time monitoring, automation, and various uses. IoT includes important parts like sensors, actuators, and cameras. Sensors, such as those for temperature, motion, and the environment, gather information from the world around them. Cameras can take pictures and videos, expanding the range of data that can be collected and studied in the IoT network.
Healthcare
The introduction of 5G technology in healthcare is transforming the industry by facilitating a range of cutting-edge applications. These include smart disability systems, heart health monitoring, and wheelchair management, which are currently under active consideration and experimentation. A particularly notable development is remote surgery, where surgeons and patients are situated in different locations. This process involves the use of specialized haptic and tactile sensor devices to capture the precise hand movements of surgeons. The data is then transmitted in real-time to a remote robot, which interprets the information and carries out surgical procedures. This showcases the potential of 5G to enable sophisticated, remote medical procedures and enhance the accessibility of healthcare services.
Agriculture
The Agricultural Environment Intelligent Monitoring System is a sophisticated solution designed for precision agriculture. It brings together a range of sensors, data analysis tools, and control systems to enhance the conditions in greenhouses and fields, leading to more effective and efficient agricultural practices.
This system incorporates an extensive sensor network in agricultural settings to collect up-to-date data on crucial factors such as air temperature, humidity, soil moisture, temperature, carbon dioxide levels, and light intensity. Additionally, video cameras provide visual information for better insights.
By automating these processes, the system ensures that the environmental conditions are precisely controlled to support optimal crop growth, all the while conserving resources. Farmers and managers can access this information remotely through mobile and computer interfaces, enabling them to monitor real-time data and make adjustments as needed.
Moreover, the system includes alert and alarm features that promptly notify users of any deviations that could potentially impact crop health and yield, allowing for swift responses to maintain the well-being of the crops.
Conclusion: A Look Towards the Future
The journey from 1G to 5G showcases the remarkable progress of wireless technology. From the limited voice calls of yesteryear to the ultra-fast, hyper-connected world of 5G, this evolution has fundamentally reshaped human communication and interaction.
As 5G continues to develop and reach its full potential, we can expect even more transformative applications and advancements across various sectors. The future of connectivity is undoubtedly bright, and 5G is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the years to come.